GDPR Data Mapping Software
Learn why data mapping is important for GDPR compliance, and how data mapping software can help you.
- Articles
- Data Mapping
- GDPR Data Mapping Tool
Data Mapping
Data mapping is a key component of GDPR documentation and compliance. It is a natural starting point in your compliance efforts because it outlines how personal data is processed and handled in your organization and the parties with whom you share data.
Importance of Data Mapping under GDPR
Data mapping in the context of GDPR is a dual exercise. The inner core focuses on how personal data is processed in your company - this is what we call 'data mapping'. The outer ring deals with how and with whom these data are shared - we refer to this as 'data flow mapping'. Both parts are important for creating an overview of personal data is processed and form the foundation of your GDPR documentation.
With the mappings, you can for instance conduct risk assessments and develop policies, and the GDPR data mapping ensures thorough documentation.
Your 'Data Map' of Internal Processing
An internal 'data map' enables you to document and illustrate how your company processes personal data. It is a key tool that provides an overview. And it is crucial when you need to report to third parties or regulatory authorities.
This documentation is often referred to as an Article 30 record. Article 30 of GDPR specifies precise requirements for the content of such a record. Further details will be elaborated later in the article. This document is most often the first thing a regulatory authority will request during an inspection.
Yet, the record also serves as a significant tool for you, as it forms the basis for your continued work with GDPR. Here are some practical uses:
-
In case of a data breach: It is essential to quickly identify the affected processes and systems. Your record helps locate which individuals and data are involved. This information is vital for your incident handling.
-
When conducting risk assessments: Under GDPR, risks to individuals must be assessed. Your data mapping provides a necessary overview of the processes and contains the data needed to assess risks. For example, the risk of processing "names" is different from processing "health information".
-
In the formulation of your privacy policy: Many of the details that need to be included in your privacy policy will be those you have already collected in your data mapping. Thus, an up-to-date and detailed 'data map' will be of great help. Use it while ensuring that your privacy policy is also updated.
Read more about mandatory GDPR documents here
These examples are some of the many ways your data mapping forms a valuable resource. It is important to understand that data mapping is not only the foundation for your GDPR documentation. It is also a practical tool that supports you in various data protection tasks.
Your 'Data Flow Map' of External Processing
For the external part of data mapping involving third parties, you must account for where data is sent. It's crucial to ensure that it is protected in accordance with GDPR.
Imagine an everyday situation. You're booking an appointment with a hairdresser and you share your personal information. As a customer, this is a common scenario. The moment the information is shared, the hairdresser becomes the 'data controller'. Although the hairdresser may have implemented security measures, their responsibility grows. This happens if they decide to use an external digital booking system. This system, operated by an IT provider, becomes a 'data processor'. Because they are managing your data on behalf of the hairdresser.
The hairdresser must document this data flow. And they need to ensure that the data processor upholds a comparable level of security. Errors in data management can make the hairdresser accountable for data breaches. This highlights the importance of mapping data flows between all involved parties.
As a data controller, it is your responsibility to have full insight into and documentation of all data flows leaving your company. Detailed data flow mapping enables you to proactively identify risks and act on them. It also allows you to prove compliance to registered individuals and regulatory authorities.
A 'personal data world map' identifies all parties you share data with. use it to maintain the highest standards of data protection. This creates trust and security. Which is fundamental for a long-lasting customer relationship based on responsibility and integrity.
What Is GDPR Data Mapping & How to Comply
In this section, I will specify which information you should include in your GDPR data mapping. I will make a distinction between two types of documentation. The first is related to your internal processing, and the second concerns your external processing.
To meet GDPR standards, data mapping is an essential activity that can be adapted to the different needs and workflows of your company. Methods for documentation vary widely. They range from traditional handwritten documents to digital solutions like Excel or Word. There also exist specialized platforms designed for data mapping. Regardless of the choice, the goal is to achieve a result that meets the requirements of GDPR. Digitalization of this process often helps to clarify, organize, and update your data mappings. Which helps you with your compliance with GDPR.
In general, you will benefit from developing a data mapping template. Gather all relevant information for the work processes where you handle personal data. This data mapping template can be based on Article 30 of GDPR. But you should consider expanding your documentation beyond the scope of this article. Collecting more information when working with your data mapping process.
A Data Mapping Template for Your Internal Processing
Article 30 of GDPR acts as a basic template for your data mapping. This article specifies the information that should be recorded. However, your data mapping should not be limited to only this article. Article 5 of GDPR addresses the principles of data processing, which include legality, fairness, and transparency. It also mandates data protection by design and by default. These principles should be integrated to cover all aspects of personal data handling.
Thus, your internal data mapping should include:
-
The purpose of processing. This should be clearly defined and legitimate, such as personnel administration or marketing.
-
Categories of registered individuals. Specify the groups of individuals whose data is processed. This could be employees or customers. You don't need to identify individual persons.
-
Types of personal data. Categorization of the data processed, divided into 'ordinary' and 'sensitive' data. For instance contact information or health information.
-
Retention periods. Specify how long data is retained. Do this with clear deletion deadlines, such as '3 years after the end of employment.'
-
Security measures. A review of the technical and organizational security measures put in place to protect personal data.
-
System integration. It is also crucial to indicate which IT systems are used for storing or processing the data. This will further clarify where and how personal data is handled. This may include CRM systems, HR software, or marketing platforms. It could also be other databases used in your data processing operations.
Expanding your data mapping beyond the requirements of Article 30 provides a deeper insight. This not only supports GDPR compliance but also promotes an understanding of how data protection can be strengthened. Ask yourself relevant questions for each process, such as:
-
What is the legal basis for processing?
-
Which data is essential to ensure the rights of the registered individuals?
Such considerations contribute to improving your handling of personal data.
Your Data Flow Mapping – What Should It Include?
Data flow mapping is a detailed visualization of the flow of personal data. These flows can be within your organization and between external parties. This process requires a deep understanding of the roles involved in data processing. Such as the data controller, data processor, and subprocessor.
As a data controller, you bear the primary responsibility for handling personal data. The data processor is the entity that processes data on your behalf and must do so in compliance with the GDPR. If a data processor delegates tasks to another processor, this entity becomes your subprocessor. This obligates you to check and manage such third parties.
In your data flow mapping, you should meticulously document the following:
For Data Processor Engagements.
A complete record of each data processor. This includes company details, the types of data shared, and the security measures taken.
Confirmation of existing data processing agreements. Details of the subprocessors’ roles are also crucial.
For international data transfers, it's important to establish and document a legal transfer basis. This could involve Standard Contractual Clauses (SCC). For U.S.-based companies, you can check if they are part of the Data Privacy Framework.
If the transfer occurs to a country outside the EU a Transfer Impact Assessment must be prepared. This helps ensure the level of data protection is maintained. If the company is part of the Data Privacy Framework, this is not needed.
Disclosures to Another Data Controller.
It is vital to establish the procedures for how data is passed on to other organizations. In cases where the recipient will act as data controller.
This can include mandatory transfers to authorities. Additionally, there could be voluntary exchanges with entities such as insurance companies.
In all cases, the legal basis for each disclosure must be explicit and clearly defined. Moreover, any transfers to third countries must be secured. This is done through appropriate transfer mechanisms.
Receiving Data from Other Data Controllers.
When your organization receives data from other data controllers, careful consideration is required. You must assess how you secure and process this information. If you act as a data processor for another organization, your procedures and security measures need to be clearly stated. Additionally, you should have the capability to demonstrate these measures. It's vital to show how you secure the data in accordance with GDPR.
Your data flow mapping is not just a tool for ensuring compliance with the law. It also serves as a resource for your organization to:
-
Account for Data Processors by creating an overview of all your data processors. This includes those located in risky third countries. Such an overview is essential to ensure compliance with the rules for data transmission within the GDPR framework.
-
Use your mapping to proactively identify potential security risks. This allows you to act in time to prevent any data breaches or compliance violations.
-
Prepare for audits by gaining a clear overview of which suppliers and subprocessors need regular checks. This is to ensure they maintain the necessary data protection standards.
Your data flow mapping has practical uses that extend beyond compliance with data protection legislation. It strengthens the overall data protection practices within your organization. This enhancement promotes trust among stakeholders, customers, and partners.
Challenges in Data Mapping
In the previous sections, I have described the approach to performing data mapping and data flow mapping. This section will highlight some of the most common challenges encountered. These are issues that various companies often face during the process of their data mapping.
A recurring challenge is that data mapping is often handled and maintained manually. This is frequently done through methods like a homemade Excel template. As a company grows and more people become involved in GDPR documentation, responsibilities tend to shift. With the increase in personal data being processed, new challenges can arise.
Here are three examples we often encounter:
Collaboration with Colleagues
To compile a comprehensive data mapping, it's necessary to gather information. This information must come from many departments within your company. This requires an enterprise-wide mapping effort. Input is needed from employees who have detailed knowledge of their respective processes. Furthermore, they must understand the personal data processed within these areas. This necessitates regularly "interviewing" your colleagues. The purpose is to update your data mapping and ensure it reflects any changes. Like the introduction of new personal data or data processors.
Updates in Legislation
A data mapping is a snapshot of your organization's data handling at a given time. Yet, laws and compliance requirements change over time. Suppose the GDPR regulation is updated, or new guidelines are issued. Then your data mapping must be updated accordingly. To do this effectively, having a well-documented and structured data map is crucial. It should allow you to quickly filter and identify the affected areas.
A recent example is the newly approved Data Privacy Framework. This framework permits the transfer of EU citizens' data to U.S.-based companies that are registered under it. In this context, you must be capable of searching your data flow map. The goal is to identify the U.S.-based companies you collaborate with. Then, you need to update the documentation for those companies that are registered under the new framework.
Overview of Your Data Flows and Processes
The complexity of your company is reflected in your GDPR data mapping. As complexity increases, the challenge of gaining an overview escalates. This makes tracking progress and identifying gaps more difficult. The documentation from your data mapping may be required in various contexts. A rigid template, like those in Excel, can limit your flexibility. Consider, for example, how one day you need to use your data mapping to compile a record. But the next day you need to gain an overview of U.S.-based IT suppliers. An inflexible data map format can make it difficult to create this overview.
This is likely why the market offers a range of specialized compliance platforms. These platforms can assist you in performing your data mapping. They also provide operational tools that offer an overview. And they can assist with management based on various use scenarios.
How Our Free GDPR Data Mapping Tool Simplifies GDPR Compliance
Some companies and data protection officers find an Excel template most optimal for their data mapping. It's important to recognize that for them, this may indeed be the best solution. This choice can be driven by various factors. These include the size of the company, and the complexity of data flows, or it may fit into existing workflows.
Yet, for many, it is a great help to have access to a GDPR data mapping tool that can guide them through the process. At .legal, we offer such a solution with our compliance platform, Privacy. This platform is designed to guide you and your colleagues through data mapping and data flow mapping tasks. Privacy then provides the overviews and reports necessary to demonstrate your GDPR compliance.
The Privacy platform operates on a subscription basis, where the first level is free. This makes Privacy a tool that is accessible to all and can be used by any company to start their data mapping. In the following, I will explain how the free version of Privacy can assist you with your GDPR data mapping.
Benefits of Automated GDPR Data Mapping
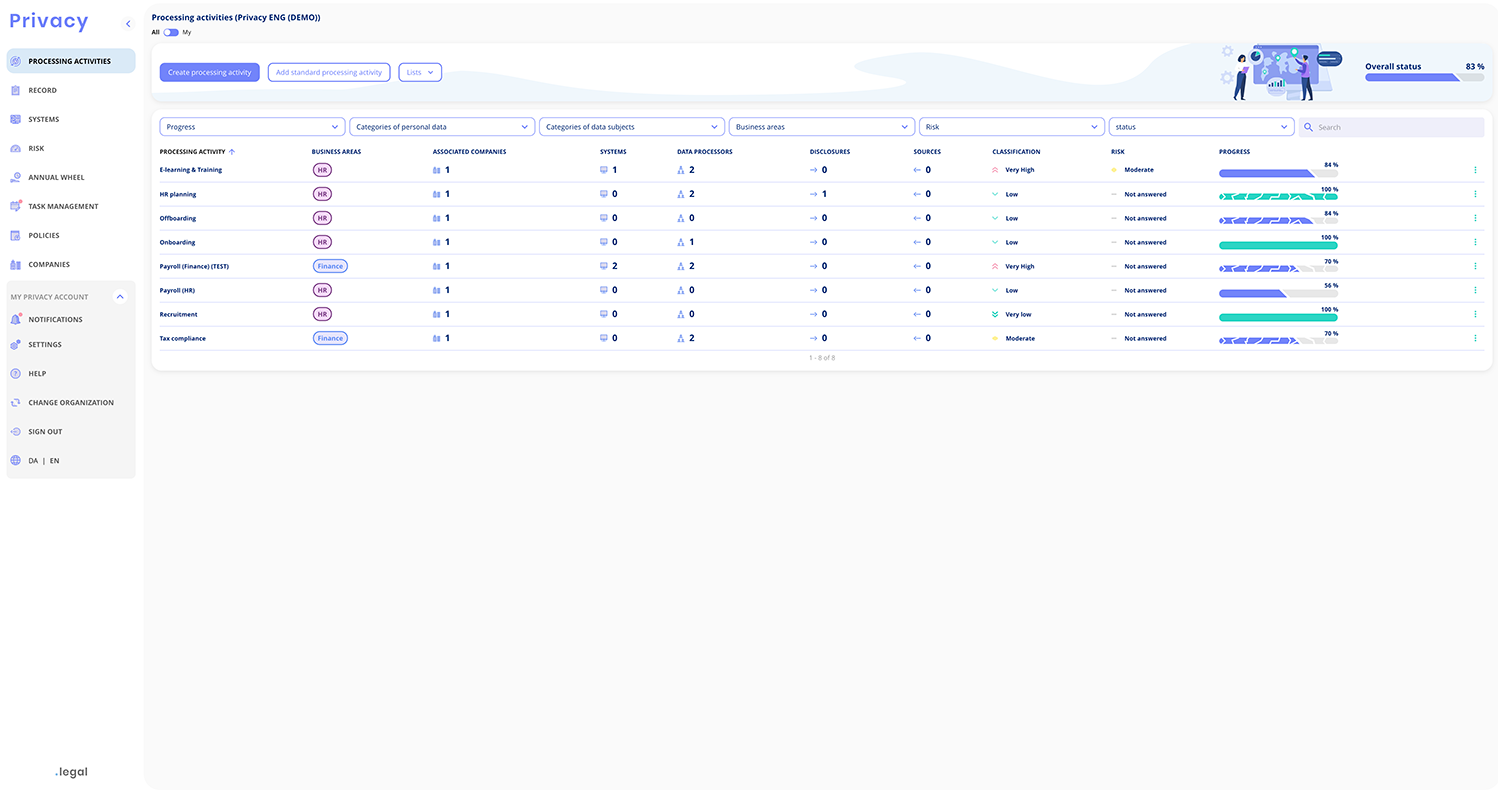
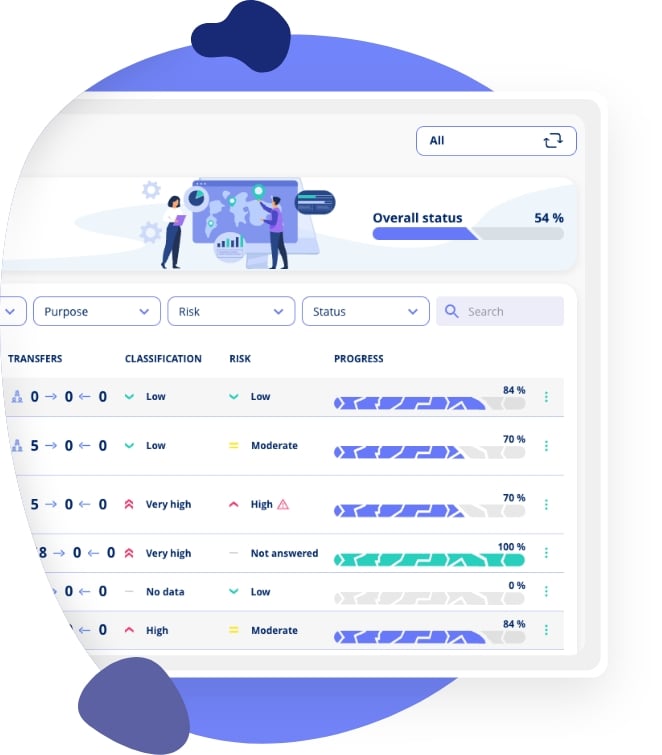
Documentation of Processing Activities
In Privacy, data mapping is referred to as 'Processing Activities'. The free version grants access to this feature. Here, you are guided through the documentation process in user-friendly steps. This ensures that all necessary information is collected and recorded correctly.
If you forget something along the way or come across missing information, the platform will alert you to these gaps. This approach ensures that you are always aware of any deficiencies in your documentation. It also provides guidance on how to complete your data mapping.
Automatically Generated Article 30 Record
Based on your data mapping in the 'Processing Activities' function, Privacy can generate an updated Article 30 record for you. This automation ensures that you always have access to a current report. You can respond quickly if a supervisory authority requests insight.
Data Flow Mapping of Different Sharing
The section on data flow mapping can seem overwhelming, especially when you need to identify who receives data and what role they play. Privacy offers a step-by-step guide that simplifies the process. It provides clarity about the different parties, the direction of data flows, and the necessary registrations. For instance, the platform will only ask you to specify a transfer basis if it is relevant to the situation.
By using Privacy for your data flow mapping, you can avoid errors and get a clear picture of how data is shared and processed in relation to your company.
And all the information you record in your data mapping in Privacy can, of course, be used for various purposes. This also means that, based on this mapping, you can also generate a list of, for example, your data processors afterward.
And All the Rest
Privacy offers many other features that can support you in your GDPR documentation tasks – all in the free version. Here you can perform risk assessments and set up your GDPR or general compliance calendar. Additionally, you can store policies, and register your systems as well as suppliers.
As with any compliance task, it is best to start somewhere and build from there. If this article has inspired you to start your GDPR data mapping and you seek guidance, consider using the free version of Privacy. You can take advantage of its features today.
FAQ: Common GDPR Data Mapping Questions
What is the primary purpose of data mapping in GDPR compliance?
The primary purpose of data mapping in GDPR compliance is to ensure a thorough understanding of where and how personal data is processed. It also involves documenting these processes within an organization. This process aids in identifying and protecting personal data, and in managing it correctly. It also ensures that the organization can comply with the requirements of the data protection regulation.
What common challenges do organizations face with manual data mapping for GDPR?
Organizations often face challenges such as a lack of clarity and the risk of errors. Additionally, they struggle with continuously updating and maintaining documentation. Ensuring accurate and consistent input from all relevant departments can be challenging.
How does GDPR data mapping facilitate Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)?
Data mapping provides a clear picture of data flows and processing activities. This clarity is essential for assessing risks and potential impacts on personal data security. This is a necessary part of conducting a DPIA.
How can businesses choose the right GDPR data mapping tools for their needs?
Businesses should select tools that suit their data complexity, size, and resources. When selecting tools for data mapping, it is recommended to consider several factors. User-friendliness and scalability are crucial. Look for the tool's ability to integrate with existing workflows. And its capability to generate reports and documentation for compliance purposes.
How do you ensure that data mapping is updated with the latest GDPR requirements?
It is crucial to stay up-to-date with the latest changes in GDPR legislation and implement these in the data mapping process. This process may involve regular revisions of the data mapping documentation. The use of tools that automatically update with legislative changes can be beneficial.
Can data mapping help identify unnecessary data collection?
A data mapping process can aid in identifying the unnecessary collection of personal data. It helps ensure that the organization processes only what is necessary. This is vital for specific and legitimate purposes.
What role does data mapping play in managing data transfers to third countries?
Data mapping is crucial for identifying data flows to third countries. It ensures that such transfers comply with GDPR's requirements for international data transmission. This includes the use of Standard Contractual Clauses (SCC) and other transfer mechanisms.
How can Privacy help small and medium-sized businesses get started with GDPR data mapping?
Privacy provides a user-friendly platform that simplifies the data mapping process. It's designed to make it easy for small and medium-sized businesses to get started. With templates and step-by-step guidance, even companies without a dedicated data protection officer can start. They can work towards achieving full GDPR compliance.
GDPR Compliance Software


.jpg)


.jpeg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)

-1.png)



.jpeg)






.jpg)

Info
.legal A/S
hello@dotlegal.com
+45 7027 0127
VAT-no: DK40888888
Support
support@dotlegal.com
+45 7027 0127
Need help?
Let me help you get started

+45 7027 0127 and I'll get you started
.legal is not a law firm and is therefore not under the supervision of the Bar Council.