What Are Processing Activities?
Even small companies are likely to have more than 10 processing activities, so it’s important to define these in a way that aligns with their everyday operations for better compliance results.
-
Definition of a Processing Activity
-
19 Examples of Processing Activities
Introduction
If your business processes customer or employee personal data – which most companies do – it’s important to understand what a processing activity is.
The term "processing activity" is central to GDPR, and being familiar with it is essential for compliance. One key requirement of GDPR is to map out and document your processing activities in a record of processing activities (RoPA), as outlined in Article 30.
Definition of Processing Activities
GDPR defines processing as: “...any operation or set of operations which is performed on personal data or on sets of personal data, whether or not by automated means, such as collection, recording, organisation, structuring, storage, adaptation or alteration, retrieval, consultation, use, disclosure by transmission, dissemination or otherwise making available, alignment or combination, restriction, erasure or destruction”. (GDPR article 4)
Put more simply, processing activities cover all activities involving personal data. This can include everything from collecting and storing to using, sharing, or deleting data. If an action involves personal data – such as names, addresses, phone numbers, or emails – it qualifies as a processing activity.
If you're unsure what personal data is, it’s worth clarifying this first.
Why Is This Important?
Processing activities are a cornerstone of GDPR compliance. Mapping and understanding how personal data flows through your organisation is essential because it reveals exactly how the data is used.
Organisations typically process data for multiple purposes, often tied to specific business operations. For example, processing invoices to ensure proper bookkeeping is a distinct activity that involves specific types of personal data.
The purpose of processing invoices is clear: they need to be recorded in an accounting system to comply with legal requirements, such as bookkeeping laws. This process is separate from other processing activities, like payroll.
By defining processes like this, you gain a clearer understanding of how data is handled across the organisation. This includes identifying who manages the data, which IT systems are involved, and other key details.
Once you’ve mapped all the personal data processing activities within your organisation, you can then review each activity to ensure it’s compliant with GDPR rules. This is why GDPR requires every organisation that processes personal data (essentially all organisations) to create and maintain a record of processing activities.
How to Identify Processing Activities
Mapping processing activities involves understanding how personal data is handled in practice. The documentation should reflect how employees actually work with data, not just theoretical workflows.
If you have only a few colleagues, mapping processing activities can be relatively straightforward. The GDPR lead can define the processes themselves or speak directly with colleagues to clarify their tasks. Alternatively, you could hold a brief session with your team to map out the organisation’s data processes collaboratively.
For businesses with 100+ employees, a more structured and inclusive approach is recommended. We've outlined this process in detail in our GDPR checklist.
Data Mapping
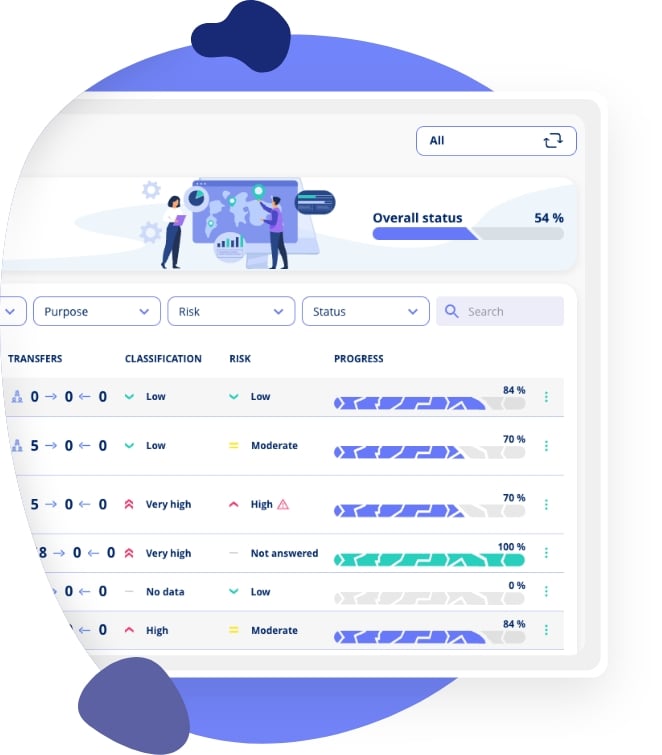
The goal of mapping all processing activities is to document your organisation’s processing activities in your record of processing activities - a legal requirement. This documentation can be done manually, using spreadsheets, or with GDPR software, which often makes the process easier to manage.
19 Examples of Processing Activities
To help illustrate what processing activities might look like in your organisation, here are 19 examples which would be representative for many organisations.
To help you get started with your GDPR compliance, these examples have already been created as templates in Privacy, allowing you to map your processing activities quickly and easily.

Document 5 processing activities, by using our templates, for free, with our GRC Platform (No need for credit card, no commitment and unlimited time on the free plan) - sign up here.
HR
HR Management
General HR tasks, such as managing employee contracts, absence records, and sick leave, involve processing personal data like national ID numbers, salary details, or health information. These activities require extra care under GDPR.
Workplace Accidents and Injuries
Registering workplace accidents involves processing sensitive personal data to comply with occupational health and safety laws and to ensure employee well-being. Workplace regulations require such incidents to be documented and reported, making this a distinct activity separate from other HR processes.
Commute Management
Managing company vehicles or employee mileage logs involves handling data about employee travel during work hours, which qualifies as personal data processing.
Travel Abroad
Organising employee travel involves processing data such as travel itineraries, passport details, and expense receipts. This activity is separate from mileage tracking, as it deals with different types of personal data, like passport information.
Recruitment
Recruitment involves processing CVs, applications, and references to evaluate candidates for potential employment. This is a separate processing activity distinct from managing data for current employees.
Security
Access control systems, such as key cards or security logs, process personal data about employees' movements and access to facilities. This activity is distinct from other HR processes, as it is focused on maintaining organisational security.
E-learning & Training
Employees often undergo E-learning training, such as awareness training and courses. Managing personal data related to these activities, such as attendance or certifications, constitutes a distinct processing activity.
Finance
Budget planning
Processing invoices and accounting data often involves personal data such as names, addresses, and payment information for customers, freelancers, or suppliers. Bookkeeping is a separate processing activity because of legal obligations to maintain financial records.
ERP system (Enterprise Resource Planning)
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems process personal data related to customers and potential customers, focusing on sales and customer relationship management. This is different from bookkeeping, which focuses on financial records.
Payroll
Payroll processing includes handling employee bank details, tax information, and other salary-related data. This is a distinct activity from invoicing, as it involves different legal requirements and data types.
Pensions and Insurance
Managing employee pension schemes and insurance policies involves processing data such as pension contributions and insurance preferences.
Marketing
Photos and Videos for Marketing
Using employee photos or videos for marketing purposes goes beyond standard employment expectations. This usually requires a separate legal basis, such as consent or legitimate interest, making it a distinct processing activity.
Content Management System (CMS)
Managing a website can involve processing personal data collected through contact forms or cookies. This activity is distinct from managing social media, as it deals with data collected directly via the organisation's own platform.
Social Media Management (SoMe)
Engaging with customers through social media campaigns or posts involves processing data on third-party platforms. This activity is separate from managing personal data collected via the company’s website.
Marketing consent
Sending newsletters by email involves processing subscribers' email addresses and other registration details. This activity is typically based on consent, such as when individuals sign up through the organisation’s website.
Daily Operations
Guest Registration
Many organisations require visitors to sign in with their name and contact details for access control purposes. This makes guest registration a processing activity, and visitors must be informed of how their data is used.
Customer Service
Business communications with partners or stakeholders often involve processing personal data, such as exchanging notes or emails.
Customer and Product Follow-Up
Following up with customers about their preferences or purchases to improve products or provide better service is a separate processing activity. This might require consent or legitimate interest as the legal basis, and customers must be informed of this specific processing.
IT Administration
Creating and managing user accounts, logging activities, and implementing access controls involves processing data about system users. These activities are designed to ensure IT security and are distinct from, for example, payroll processing, even though both involve employee data.
Conclusion
Understanding what processing activities are and how they differ is essential for GDPR compliance. Properly mapping your organisation’s activities ensures that your documentation aligns with real-world processes of your organisation.
This foundation will be important for ensuring personal data is processed securely and lawfully as you continue improving your GDPR compliance. By treating each processing activity as a distinct workflow, you make it significantly easier to address compliance challenges and maintain data protection standards across your organisation.
GDPR Compliance Software


.jpg)


.jpeg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)

-1.png)



.jpeg)






.jpg)

Info
.legal A/S
hello@dotlegal.com
+45 7027 0127
VAT-no: DK40888888
Support
support@dotlegal.com
+45 7027 0127
Need help?
Let me help you get started

+45 7027 0127 and I'll get you started
.legal is not a law firm and is therefore not under the supervision of the Bar Council.